Hair loss can occur due to a variety of factors: health, genetics and environmental. If your hair loss is due to genetics, it’s called androgenetic alopecia. Health related issues like hormonal changes, medical conditions such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases, stress, certain medications, and improper hair care practices can also causes of hair loss.
Understanding the underlying cause is crucial in determining the most effective treatment for hair loss.
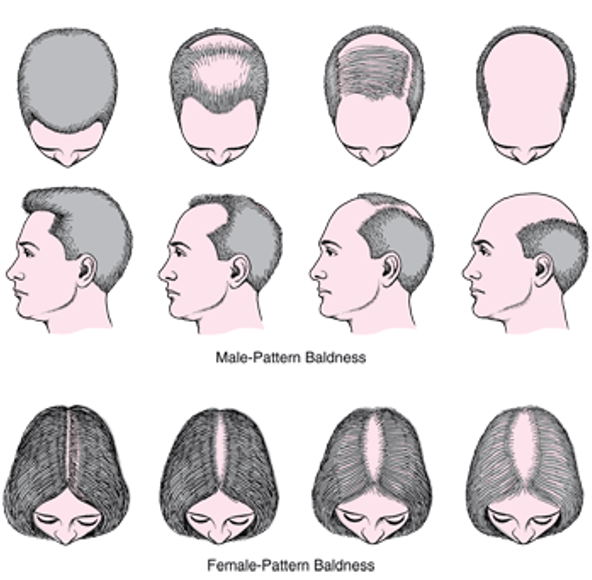

Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can be a distressing condition that affects individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. While it’s normal to shed 100-150 hairs daily as part of the natural hair growth cycle, excessive or sudden hair loss may indicate an underlying issue.
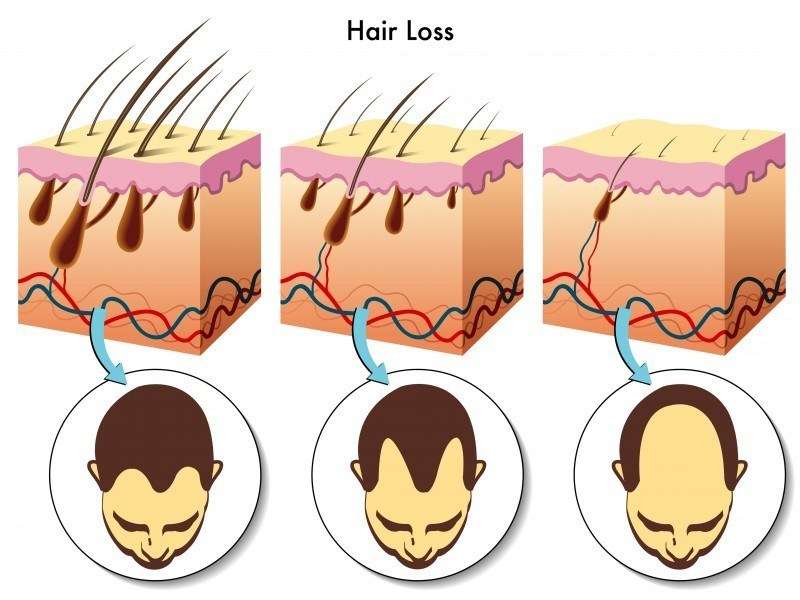
One of the most common causes of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This hereditary condition is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, typically starting at the temples or crown in men and resulting in a distinct pattern of baldness. In women, it often manifests as diffuse thinning over the crown and top of the scalp, preserving the hairline. Androgenetic alopecia is influenced by genetic predisposition and hormonal factors, particularly the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can miniaturize hair follicles over time.
Hormonal changes can contribute to hair loss in both men and women. Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause, can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle and lead to temporary hair shedding or thinning. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders, which affect hormone levels, can also contribute to hair loss.
Various medical conditions can cause or contribute to hair loss. These include:
Lifestyle factors can also play a role in hair loss. These include:
As we age, the rate of hair growth slows down, and the hair follicles shrink, leading to thinner, finer hair. Additionally, hormonal changes associated with aging, particularly in menopause for women and declining testosterone levels for men, can contribute to hair loss
Hair loss, medically termed alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions worldwide. It can manifest in various forms, including gradual thinning, patchy bald spots, or complete baldness. Hair loss can impact both men and women, often causing psychological distress and affecting self-esteem. While some types of hair loss are temporary and reversible, others may be permanent without proper intervention. Seeking early diagnosis and treatment is essential in managing hair loss effectively.
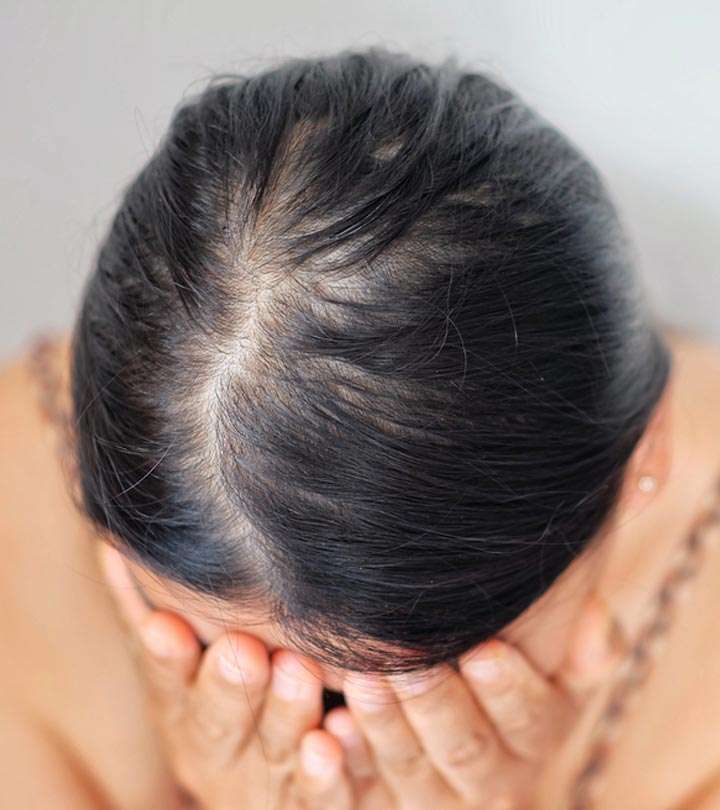

Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. While it’s often associated with aging, hair loss can occur at any stage of life and may be temporary or permanent.
Hair is composed of a protein called keratin and grows from hair follicles embedded in the scalp. Each hair follicle goes through a cycle of growth, transition, and resting phases, known as the hair growth cycle. The length and thickness of hair are determined by genetics, while factors such as hormones, nutrition, and overall health influence hair growth and quality.
Diagnosing the underlying cause of hair loss typically involves a medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests, such as blood tests or scalp biopsies. Treatment options for hair loss vary depending on the cause and may include:
Hair loss can have a significant psychological impact on individuals, affecting self-esteem, body image, and quality of life. Make sure to love yourself throughout the process.
Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is the predominant form of hair loss in men. Characterized by a distinct pattern of thinning hair, it often starts with a receding hairline and progresses to baldness at the crown. Genetics and the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) primarily influence male hair loss. While aging is a natural factor, treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants can slow or reverse its course.
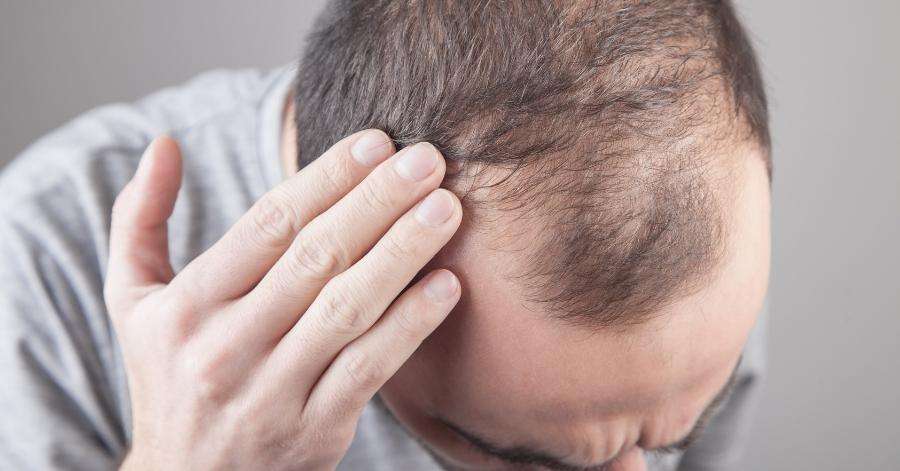

Hair loss is a common concern among men, with male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, being the most prevalent form. This condition typically follows a predictable pattern, starting with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, eventually leading to partial or complete baldness. Let’s delve deeper into the causes, patterns, and treatment options for men’s hair loss:
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness:
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in male pattern baldness. It’s often inherited from either side of the family and can manifest at any age, with some men experiencing hair loss as early as their late teens or early twenties.
Hormonal Factors: The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a key player in male pattern baldness. DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing new hair. This hormonal imbalance can be influenced by genetics and aging.
Age: While male pattern baldness can occur at any age, it’s more commonly observed as men get older. As men age, their hair follicles may become more sensitive to DHT, leading to gradual thinning and balding.
Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle choices such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor nutrition, and high stress levels can contribute to hair loss or exacerbate existing conditions.
Patterns of Hair Loss:
Male pattern baldness typically progresses in distinct stages, following a specific pattern known as the Norwood scale:
Treatment Options for Male Pattern Baldness:
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil, commonly known as Rogaine, is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp to stimulate hair growth. It works by widening hair follicles, prolonging the growth phase, and promoting thicker, fuller hair. Minoxidil is available over-the-counter and requires consistent, long-term use for optimal results.
Oral Medications: Finasteride, sold under the brand name Propecia, is an oral medication that inhibits the production of DHT, the hormone responsible for hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride can slow down hair loss, increase hair density, and promote regrowth. However, it may cause side effects such as decreased libido and erectile dysfunction in some men.
Hair Transplant Surgery: Hair transplant surgery involves transplanting hair follicles from donor areas (typically the back or sides of the head) to areas of baldness or thinning. This procedure can provide long-lasting, natural-looking results, but it’s important to consult with a qualified surgeon to determine candidacy and discuss expectations.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT is a non-invasive treatment option that uses low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles, increase blood flow to the scalp, and promote hair growth. While the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, some studies suggest that LLLT may be effective in slowing down hair loss and improving hair density
Hair loss in women differs from men and can stem from various causes, including hormonal fluctuations, genetics, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. Female pattern hair loss typically manifests as overall thinning rather than specific patterns seen in men. Treatment options range from topical minoxidil to hormone therapy and addressing underlying health issues.

Hair loss can be a distressing experience for women, often presenting differently from men and requiring tailored treatment approaches. Let’s explore the causes, patterns, and treatment options for women’s hair loss:
Causes of Hair Loss in Women:
Hormonal Factors: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can contribute to hair loss in women. Hormonal imbalances can affect the hair growth cycle, leading to excessive shedding or thinning.
Genetics: Female pattern hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, can be inherited from either parent. While less common than in men, it can still lead to progressive thinning of the hair, primarily at the crown and temples.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as alopecia areata, autoimmune disorders, and scalp infections, can cause hair loss in women. Additionally, underlying health issues like iron deficiency anemia or hormonal disorders may contribute to hair thinning.
Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as stress, poor nutrition, crash dieting, excessive styling or chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles can all contribute to hair loss or exacerbate existing conditions.
Patterns of Hair Loss in Women:
Unlike men, who often experience distinct patterns of balding, hair loss in women typically presents as overall thinning or diffuse shedding throughout the scalp. Female pattern hair loss may involve widening of the part, noticeable thinning at the crown, or a reduction in hair density all over the scalp.
Treatment Options for Women’s Hair Loss:
Topical Treatments: Minoxidil, available over-the-counter as Rogaine, is a topical solution that can help stimulate hair growth in women. Applied directly to the scalp, minoxidil works by widening hair follicles, prolonging the growth phase, and promoting thicker, fuller hair.
Hormone Therapy: For women experiencing hormonal imbalances contributing to hair loss, hormone therapy may be prescribed. This may involve oral contraceptives containing estrogen and progestin or hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopausal women.
Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients essential for hair health, such as biotin, iron, and zinc, may help support hair growth and reduce shedding in women with nutritional deficiencies.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. This procedure can help improve hair density and thickness in women with thinning hair.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT uses low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles, increase blood flow to the scalp, and promote hair growth. This non-invasive treatment option may be effective in slowing down hair loss and improving hair density in women.
Minoxidil, commonly known as Rogaine, is a topical medication approved by the FDA for treating hair loss. Originally developed as an oral medication for hypertension, its hair-growing properties were discovered as a side effect. Minoxidil works by widening the hair follicles, prolonging the hair growth phase, and stimulating hair regrowth. It’s available over-the-counter in various strengths and formulations for both men and women. Consistent use is necessary to maintain results, and it may take several months before noticeable improvements are seen.
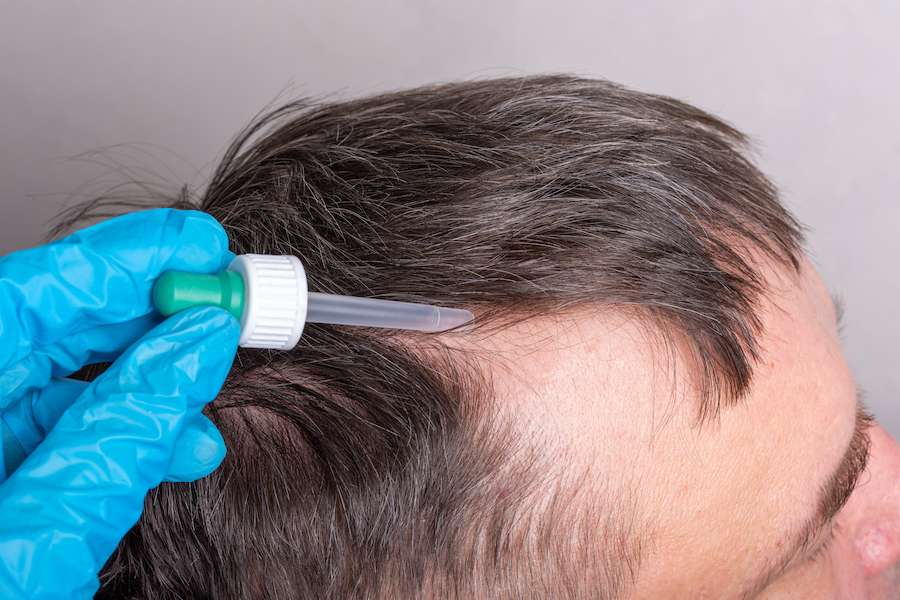
Minoxidil, commonly known by the brand name Rogaine, is a topical medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of hair loss. It has been a staple in the arsenal against hair loss for decades, offering hope and results to millions of individuals experiencing thinning hair or baldness. Let’s explore what makes minoxidil a trusted solution for hair loss:
How Minoxidil Works:
Minoxidil’s mechanism of action in promoting hair growth is not fully understood, but it is believed to widen hair follicles, prolong the hair growth phase (anagen), and stimulate hair regrowth. Additionally, minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, delivering essential nutrients to the hair follicles and creating an optimal environment for hair growth.
Benefits of Minoxidil:
Effective for Both Men and Women: Minoxidil is approved for use in both men and women, making it a versatile option for individuals of all genders experiencing hair loss.
Convenience: Available over-the-counter in various formulations, including solutions, foams, and sprays, minoxidil offers convenience and flexibility in application. It can be easily incorporated into daily grooming routines without disrupting lifestyle or activities.
Minimal Side Effects: Minoxidil is generally well-tolerated, with few reported side effects. The most common side effect is scalp irritation, which is usually mild and temporary. Allergic reactions or systemic side effects are rare but should be monitored.
Noticeable Results: With consistent use, many individuals experience noticeable improvements in hair density, thickness, and regrowth. While results may vary, minoxidil has been clinically proven to effectively slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in a significant percentage of users.
How to Use Minoxidil:
Choose the Right Formulation: Minoxidil is available in various strengths and formulations. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable option based on your specific needs and preferences.
Apply as Directed: Follow the instructions provided on the product packaging or as directed by your healthcare provider. Typically, minoxidil is applied directly to the scalp once or twice daily, depending on the formulation.
Be Patient and Persistent: Hair regrowth with minoxidil may take time, and results are not immediate. Consistent, long-term use is necessary to maintain and maximize benefits. It may take several months before noticeable improvements are seen.
Monitor for Side Effects: While rare, it’s essential to be vigilant for any signs of scalp irritation, allergic reactions, or systemic side effects. Discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional if any adverse reactions occur.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone derived from testosterone that plays a significant role in hair loss, particularly in male pattern baldness. DHT blockers are medications that inhibit the conversion of testosterone into DHT, thereby reducing its effects on the hair follicles. Finasteride and dutasteride are two commonly prescribed DHT blockers for treating hair loss in men. By blocking DHT, these medications can slow down or stop the progression of hair loss and, in some cases, promote hair regrowth. However, they may have potential side effects and require ongoing use to maintain results.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) blockers are medications designed to inhibit the effects of DHT, a hormone implicated in the development of male pattern baldness and other forms of hair loss. By targeting DHT, these blockers aim to slow down or halt the progression of hair loss and, in some cases, promote hair regrowth. Let’s explore the role of DHT blockers in combating hair loss:
Understanding DHT and Hair Loss:
DHT is a potent androgen derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. It plays a crucial role in the development of male characteristics but can also contribute to hair loss by binding to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hairs. In individuals genetically predisposed to hair loss, excessive levels of DHT can lead to miniaturization of hair follicles and eventual cessation of hair growth.
Benefits of DHT Blockers:
Inhibition of DHT Production: DHT blockers work by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, thereby reducing the conversion of testosterone into DHT. By lowering DHT levels in the scalp, these medications help mitigate its harmful effects on hair follicles, preserving their function and promoting healthier hair growth.
Slowing Hair Loss Progression: By interrupting the underlying mechanisms of hair loss, DHT blockers can slow down or even halt the progression of male pattern baldness. This can help individuals maintain their existing hair density and delay the onset of baldness.
Promotion of Hair Regrowth: In some cases, DHT blockers may also stimulate hair regrowth by rejuvenating miniaturized hair follicles and promoting the growth of thicker, healthier hairs. While not everyone responds to treatment in the same way, many individuals experience noticeable improvements in hair density and quality over time.
Compatibility with Other Treatments: DHT blockers can be used in conjunction with other hair loss treatments, such as minoxidil or hair transplant surgery, to enhance results and optimize outcomes. Combining multiple approaches to hair restoration may provide a synergistic effect, yielding superior results compared to individual treatments alone.
Common DHT Blockers:
Finasteride (Propecia): Finasteride is an oral medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of male pattern baldness. It works by selectively inhibiting the Type II isoform of 5-alpha-reductase, thereby reducing DHT levels in the scalp. Finasteride has been shown to effectively slow down hair loss, increase hair density, and promote regrowth in a significant percentage of men.
Dutasteride: Dutasteride is another oral medication that inhibits both Type I and Type II isoforms of 5-alpha-reductase, resulting in a more comprehensive suppression of DHT levels compared to finasteride. While not FDA-approved for hair loss, dutasteride is sometimes prescribed off-label for this purpose, particularly in cases where finasteride has been ineffective.
Considerations and Side Effects:
While DHT blockers can be effective in combating hair loss, they may also be associated with certain side effects. These can include sexual side effects such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders, which may occur in a small percentage of users. Additionally, pregnant women should avoid handling crushed or broken tablets of finasteride or dutasteride due to the risk of birth defects in male fetuses.
Finasteride, sold under the brand name Propecia, is an oral medication approved by the FDA for treating male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone implicated in hair loss. By lowering DHT levels, finasteride can slow down hair loss, increase hair density, and promote regrowth in some men. However, it’s important to note that finasteride may cause side effects such as decreased libido and erectile dysfunction in a small percentage of users. Regular consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended for those considering finasteride treatment.
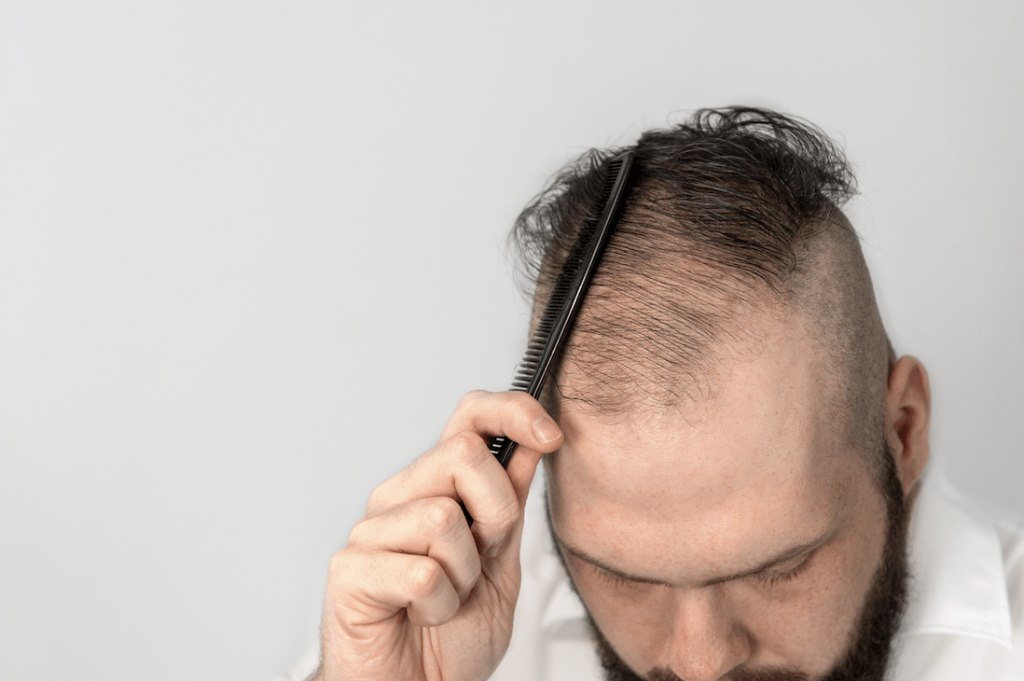

Finasteride: A Proven Solution for Male Pattern Baldness
Finasteride, commonly marketed under the brand name Propecia, is an oral medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of male pattern baldness. It is widely regarded as one of the most effective and popular treatments for combating hair loss in men. Let’s delve into the key aspects of finasteride and its role in addressing male pattern baldness:
How Finasteride Works:
Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a potent androgen hormone that plays a central role in the miniaturization of hair follicles and the progression of male pattern baldness. By blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, finasteride reduces DHT levels in the scalp, thereby preventing further hair follicle shrinkage and preserving existing hair.
Benefits of Finasteride:
Slows Down Hair Loss: Clinical studies have demonstrated that finasteride effectively slows down the progression of male pattern baldness. Many men experience a reduction in hair shedding and a stabilization of hair loss within the first few months of treatment.
Promotes Hair Regrowth: In addition to preventing further hair loss, finasteride has been shown to promote hair regrowth in a significant percentage of men. New hair growth may be observed in areas of the scalp that have experienced recent thinning, leading to increased hair density and coverage over time.
Convenient Oral Administration: Finasteride is taken orally in the form of a once-daily tablet, making it a convenient and straightforward treatment option for men with male pattern baldness. It can be easily incorporated into daily routines without disrupting lifestyle or activities.
Long-Term Efficacy: Studies have indicated that the benefits of finasteride persist over the long term, with continued use resulting in sustained improvements in hair density and quality. Consistent, ongoing treatment is necessary to maintain results, as discontinuing finasteride may lead to a gradual reversal of its effects
Dutasteride is a medication similar to finasteride but with a more potent inhibitory effect on DHT. While not FDA-approved for treating hair loss, dutasteride is sometimes prescribed off-label for this purpose, particularly in cases where finasteride has been ineffective. Dutasteride works by blocking both Type I and Type II 5-alpha-reductase enzymes, which are responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. This dual inhibition results in a more comprehensive suppression of DHT levels compared to finasteride. However, like finasteride, dutasteride may cause side effects and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Dutasteride: A Comprehensive Approach to Treating Male Pattern Baldness
Dutasteride, also known by its brand name Avodart, is a medication that offers a potent solution for combating male pattern baldness. While not FDA-approved specifically for hair loss, dutasteride is sometimes prescribed off-label for this purpose, particularly in cases where other treatments like finasteride have been ineffective. Let’s explore the key aspects of dutasteride and its role in addressing male pattern baldness:
How Dutasteride Works:
Similar to finasteride, dutasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, albeit with a broader spectrum of activity. While finasteride selectively inhibits the Type II isoform of 5-alpha-reductase, dutasteride inhibits both Type I and Type II isoforms, resulting in a more comprehensive suppression of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels in the scalp. By blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, dutasteride helps to prevent further hair follicle miniaturization and preserve existing hair.
Benefits of Dutasteride:
Comprehensive DHT Suppression: By inhibiting both Type I and Type II isoforms of 5-alpha-reductase, dutasteride offers a more thorough and robust blockade of DHT production compared to finasteride. This broader spectrum of activity may lead to greater reductions in DHT levels in the scalp and more significant improvements in hair growth.
Potent Hair Loss Prevention: Clinical studies have suggested that dutasteride is highly effective in slowing down the progression of male pattern baldness. Many individuals experience a reduction in hair shedding and a stabilization of hair loss, with some even achieving noticeable regrowth of hair.
Flexible Dosage Options: Dutasteride is available in various dosage strengths, allowing for flexibility in treatment regimens. While the standard dose is typically 0.5 mg daily, some individuals may benefit from lower doses or intermittent dosing schedules to minimize potential side effects.
Potential for Hair Regrowth: In addition to preventing further hair loss, dutasteride has the potential to promote hair regrowth in men with male pattern baldness. New hair growth may be observed in areas of the scalp that have experienced recent thinning, leading to increased hair density and coverage over time.
Considerations and Side Effects:
Despite its efficacy, dutasteride may be associated with certain side effects, similar to finasteride. These can include sexual side effects such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders, though they tend to occur infrequently. As with any medication, it’s essential to discuss potential risks and benefits with a healthcare professional before starting dutasteride treatment
We like to consider Hair Loss Solutions to be, your premier destination for restoring your hair’s vitality.
Being the pioneers in Eastern Canada, we’re thrilled to introduce NeoGraft® FUE hair transplants and other hair loss services.
Join us at Hair Loss Solutions, where innovation meets expertise, and let us help you regain your confidence. Experience the future of hair restoration with our dedicated team by your side.
info@hairlosssolutionsmoncton.com
Phone : +1 (506) 743-3768
855 Dieppe Blvd, Dieppe, NB E1A 8S6, Canada | Unit 5
Copy right © reserved by Hair Loss Solutions | Designed by Markmiz