Hair transplants offer a life-changing solution for those suffering from hair loss, providing natural-looking results and improved confidence. However, like any surgical procedure, hair transplantation comes with potential risks and side effects. One such complication is folliculitis, an inflammation of the hair follicles. Understanding folliculitis after a hair transplant is crucial for optimal recovery and maintaining healthy, vibrant hair.
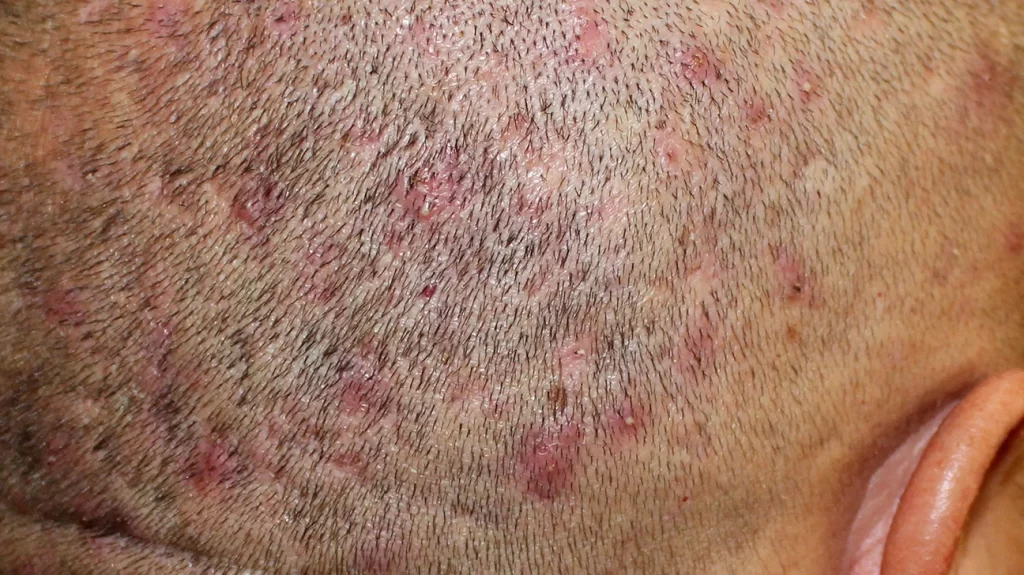
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the hair follicles. It appears as small, red bumps or pustules around the hair follicles, often resembling acne. Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, including the scalp.
Several factors contribute to the development of folliculitis following a hair transplant:
Bacterial Infection: The most common cause is a bacterial infection, typically by Staphylococcus aureus. During the transplant process, bacteria can enter the hair follicles, leading to infection.
Irritation: The scalp is sensitive post-transplant, and the use of certain hair products, tight hats, or excessive sweating can irritate the scalp, causing folliculitis.
Ingrown Hairs: Newly transplanted hair can sometimes grow back into the scalp, leading to inflammation and the development of folliculitis.
Immune Response: In some cases, the body may react to the transplanted follicles as foreign objects, triggering an immune response that results in folliculitis.
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing folliculitis:
Maintain Proper Hygiene: Keep the scalp clean by following the post-operative care instructions provided by your surgeon. Gently wash your hair with a mild, non-irritating shampoo to remove dirt and bacteria.
Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of harsh hair products, tight headgear, and activities that cause excessive sweating, especially in the initial weeks after the transplant.
Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Adhere to your surgeon’s guidelines for post-operative care, including the use of prescribed medications and ointments.
Monitor Your Scalp: Regularly inspect your scalp for any signs of infection or irritation and consult your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms.
If folliculitis occurs despite preventive measures, it can be effectively treated:
Topical Antibiotics: Your doctor may prescribe antibiotic creams or ointments to combat bacterial infections.
Oral Antibiotics: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection.
Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help soothe irritation and reduce swelling.
Anti-inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can alleviate pain and discomfort.
Avoid Picking or Scratching: Refrain from scratching or picking at the bumps to prevent further irritation and potential scarring.
While folliculitis can be a concerning side effect of hair transplantation, understanding its causes, prevention, and treatment options can ensure a smooth recovery and the best possible outcome. By adhering to proper post-operative care and seeking timely medical advice, you can minimize the risk of folliculitis and enjoy the full benefits of your hair transplant.
We like to consider Hair Loss Solutions to be, your premier destination for restoring your hair’s vitality.
Being the pioneers in Eastern Canada, we’re thrilled to introduce NeoGraft® FUE hair transplants and other hair loss services.
Join us at Hair Loss Solutions, where innovation meets expertise, and let us help you regain your confidence. Experience the future of hair restoration with our dedicated team by your side.
info@hairlosssolutionsmoncton.com
Phone : +1 (506) 743-3768
855 Dieppe Blvd, Dieppe, NB E1A 8S6, Canada | Unit 5
Copy right © reserved by Hair Loss Solutions | Designed by Markmiz